The Drosophila melanogaster suppressor of sable gene, su(s), encodes a novel, 150-kDa nuclear RNA binding protein, SU(S), that negatively regulates RNA accumulation from mutant alleles of different genes which have transposon insertions within the 5′ transcribed area.
On this examine, we delineated the RNA binding area of SU(S) and evaluated its relevance to SU(S) perform in vivo.
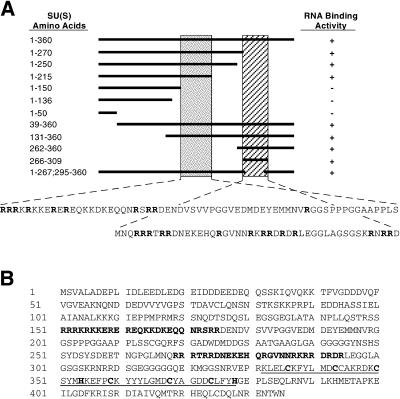
Because of this, now we have outlined two arginine-rich motifs (ARM1 and ARM2) that mediate the RNA binding exercise of SU(S). ARM1 is required for in vitro high-affinity binding of SU(S) to small RNAs that had been beforehand remoted by SELEX (binding web site choice assay) and that comprise a typical consensus sequence.
ARM1 can also be required for the affiliation of SU(S) with larval polytene chromosomes in vivo. ARM2 promotes binding of SU(S) to SELEX RNAs that lack the consensus sequence and apparently is neither vital nor enough for the steady polytene chromosome affiliation of SU(S). Use of the GAL4/UAS system to drive ectopic expression of su(s) cDNA transgenes revealed two beforehand unknown properties of SU(S).
First, overexpression of SU(S) is deadly. Second, SU(S) negatively regulates expression of su(s) intronless cDNA transgenes, and the ARMs are required for this impact. Contemplating these and former outcomes, we suggest that SU(S) binds to the 5′ area of nascent transcripts and inhibits RNA manufacturing in a fashion that may be overcome by splicing complicated meeting.
[Mutational analysis of the CytR protein binding site within the regulatory region of Escherichia coli udp gene].
Web site-specific mutagenesis of the pentameric motif TGCAA throughout the regulatory area of the udp gene with coordinates -68 and -64 relative to the transcription initiation web site was carried out.
9 mutant promoters containing a number of nucleotide base-pair substitutions on this pentameric motif had been remoted and characterised.
One mutant contained a deletion of the C/G nucleotide pair within the -66 place. Remoted mutant promoters had been cloned right into a low-copy-number expression vector pJEL250 to find out the extent of their expression, relying on the allelic state of cytR and cya genes.
The extent of CytR-dependent regulation of the udp gene and the power to titrate the CytR repressor in vivo had been proven to be drastically decreased in all mutant promoters remoted. On the idea of those outcomes, it’s concluded that the pentameric motif TGCAA performs a key position in binding the CytR repressor protein to the udp gene promoter.
